skip to main |
skip to sidebar
To configure Outlook 2007 for your Gmail address:
1. Enable POP in your email account. Don't forget to click Save Changes when you're done.
2. Open Outlook.
3. Click the Tools menu, and select Account Settings...
4. On the E-mail tab, click New...
5. If you are prompted to Choose E-mail Service, select Microsoft Exchange, POP3, IMAP, or HTTP, and click Next.
6. Fill in all necessary fields to include the following information:
Your Name: Enter your name as you would like it to appear in the From: field of outgoing messages.
Email Address: Enter your full Gmail email address (username@gmail.com). Google Apps users, enter your full address in the format username@your_domain.com.
Password: Enter your email password.
Manually configure server settings or additional server types: Leave this option unchecked if you want to automatically configure Outlook 2007. If you want to manually configure Outlook 2007, check this box now. Google Apps users should configure manually as follows.
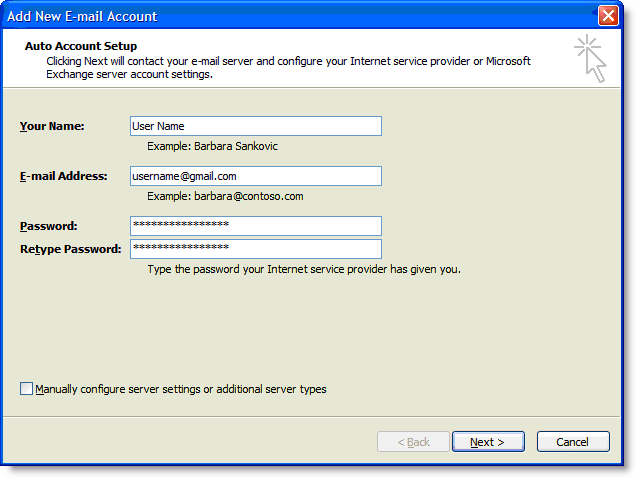
Enter name, email address, and password
7. Click Next. If you are configuring Outlook 2007 automatically, you're done! Just click Finish.
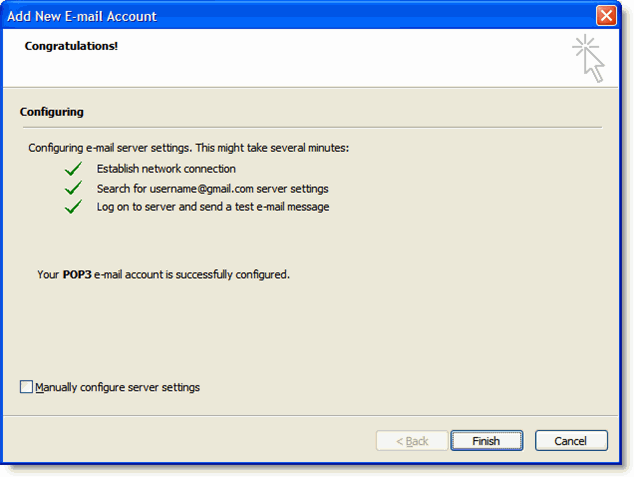
Successful Configuration
8. If you are configuring Outlook 2007 manually, select Internet E-mail and click Next.
9. Verify your User Information, and enter the following additional information:
Server Information
Account Type: POP3
Incoming mail server: pop.gmail.com (Google Apps users, enter the server names provided, don't add your domain name in these steps)
Outgoing mail server (SMTP): smtp.gmail.com
Logon Information
User Name: Enter your Gmail username (including @gmail.com). Google Apps users, enter your full address in the format username@your_domain.com
Password: Enter your email password.
Require logon using Secure Password Authentication (SPA): Leave this option unchecked.
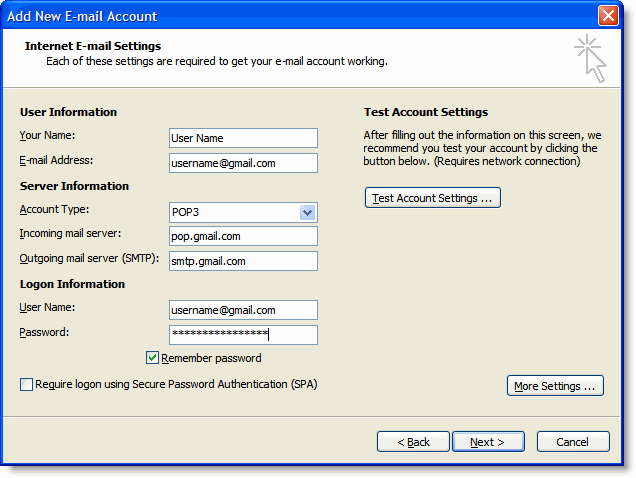
10. Account Settings Click the More Settings... button, and select the Outgoing Server tab.
11. Check the box next to My outgoing server (SMTP) requires authentication and select Use same settings as my incoming mail server.
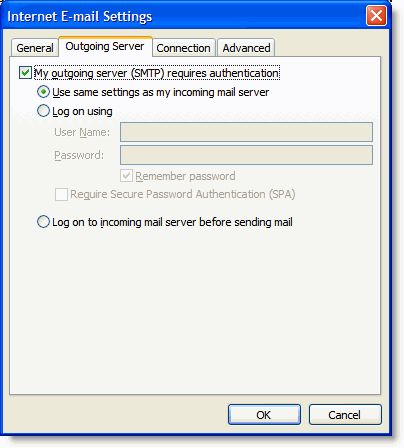
Outgoing Server Tab
12. Click the Advanced tab, and check the box next to This server requires an encrypted connection (SSL) under Incoming Server (POP3). enter 995 in POP3
13. In the Outgoing server (SMTP) box, enter 587, and select TLS from the drop-down menu next to Use the following type of encrypted connection:
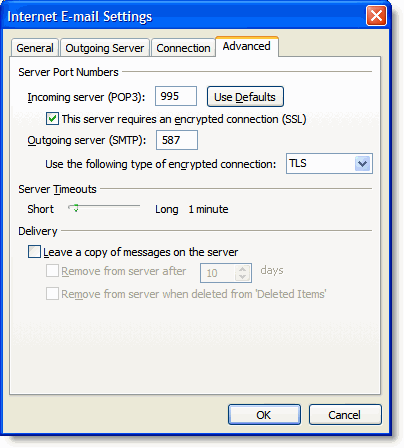
Advanced Tab
14. Click OK.
15. Click Test Account Settings... After receiving 'Congratulations! All tests completed successfully', click Close.
16. Click Next, and then click Finish.
Congratulations! You're done configuring your client to send and retrieve Gmail messages.

In computer jargon, the speed at which data is written to (or read from) an optical disc (like a CD or a DVD) is shown as a multiple of X. For example, writing to a DVD at 8X will be much faster than writing to it at 4X.[1]

CD, DVD and Blu-ray writing speeds
Modern Compact Discs support a writing speed of 52X and higher, and some modern DVDs support writing at 16X or higher. It is important to notice that the speed of 1X in CD writing is not the same as the speed of 1X when writing to a DVD. When writing to a DVD at 1X, the data is transferred at a speed of approximately 1.32 MB/s (1,385,000 bytes per second)[2]; in contrast, at single speed (1x) a recorder writes 150 KB (153,600 bytes) of data (CD-ROM Mode 1) per second [3]. Thus, in brief, one X in DVD writing speeds is about 9 times more than one X in CD writing speeds. However, these speeds are not constant, and depend on the type of data written to the disc.[4]
For Blu-ray disks, 1x speed is defined as 36 megabits per second (Mbit/s), which is equal to 4.5 megabytes per second (MB/s).[5] However, as the minimum required data transfer rate for Blu-ray movie disks is 54 Mbit/s, the minimum reading speed for a Blu-ray drive intended for commercial movie playback should be 2X.
Historically, the 1X writing speed is equivalent to the 1X reading speed, which in turn represents the speed at which a media can be entirely read in 74 minutes. Those 74 minutes come from the maximum play time that the Red Book (audio CD standard) specified for a digital audio CD (CD-DA), although nowadays most recordable CDs can hold 80 minutes. The DVD and Blu-ray discs have higher capacity, so reading or writing those discs in the same 74 minutes incurs a higher data transfer rate.
Theoretical versus practical writing speed
Almost all of the modern CD/DVD burning software support selection of the speed at which the portable disc is written to. However, the option a user choses only defines the theoretical maximum of disc burning process. There are other factors that influence the time taken for a disc to be written to:
* Resources available to the program: Reading or writing data on a disc consumes moderate to high level of system resources (including memory and CPU resources), and running other programs at the same time may force the CD/DVD drive to choose a lower speed automatically, to accommodate with the available resources.
* Disc quality: Optical disc recorders detect the available speed options based on the data which is available on the disc itself; however, some low quality discs make a high speed option available to the software, while the burning process can never reach that speed in act.
* The reading and writing process does not happen at a steady speed. Both CD and DVD store data with constant linear velocity, so outer tracks contain more data per radian than inner tracks. During reading and writing, data flow speed varies based on the position of the laser under the disc.
Choosing the best writing speed
Choosing a higher writing speed will result in a faster disc burn, but for audio CDs the quality will be lower. For optimal results burn at the media's rated speed
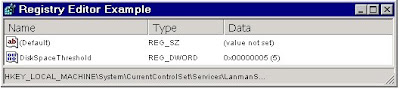
By default, Windows posts an alert when the amount of free space remaining on your hard disk falls below 10 percent.
To alter this behavior, edit:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services \LanmanServer\Parameters
Add Value DiskSpaceThreshold with a type of REG_DWORD and set it to the percentage of free disk space remaining before an alert is sent. The allowable range is 0 - 99 percent.
Key: [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters]
Value Name: DiskSpaceThreshold
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Data: 0 - 99








